
Franco Brutti
Have you ever heard of social engineering?
Social engineering has already become one of the techniques preferred by hackers to exploit human error and hack even the most complex cybersecurity systems.
Social engineering techniques are becoming increasingly sophisticated. Therefore, cybersecurity specialists, as well as their systems, must become better and better in this area.
In this article, we will tell you everything you need to know. In addition, we will tell you which techniques are most commonly used and how to avoid them.
BONUS: We will also give you tips on how to protect your information and avoid computer attacks.
And if you are interested in specializing in cybersecurity, we will tell you about its role in ethical hacking and cybersecurity.
What is social engineering and how does it work?
Social engineering comprises all techniques for manipulating and exploiting human error.
In other words, practices, and strategies to manipulate and deceive users to hack systems, steal information, and perpetrate cyberattacks.
In turn, techniques to make users reveal all kinds of confidential information, from passwords to credentials. Likewise, to grant access and release computer viruses.
In other words: hacking systems by manipulating the user.
Social engineering is one of the most successful hacking techniques for one simple reason: human error is inevitable.
No matter how large, secure, or complex the security system, human error is and will be its greatest vulnerability. In other words, users are the weakest link.
And that’s why, before we know how to avoid it, we need to understand how it works and how it’s used in real life.
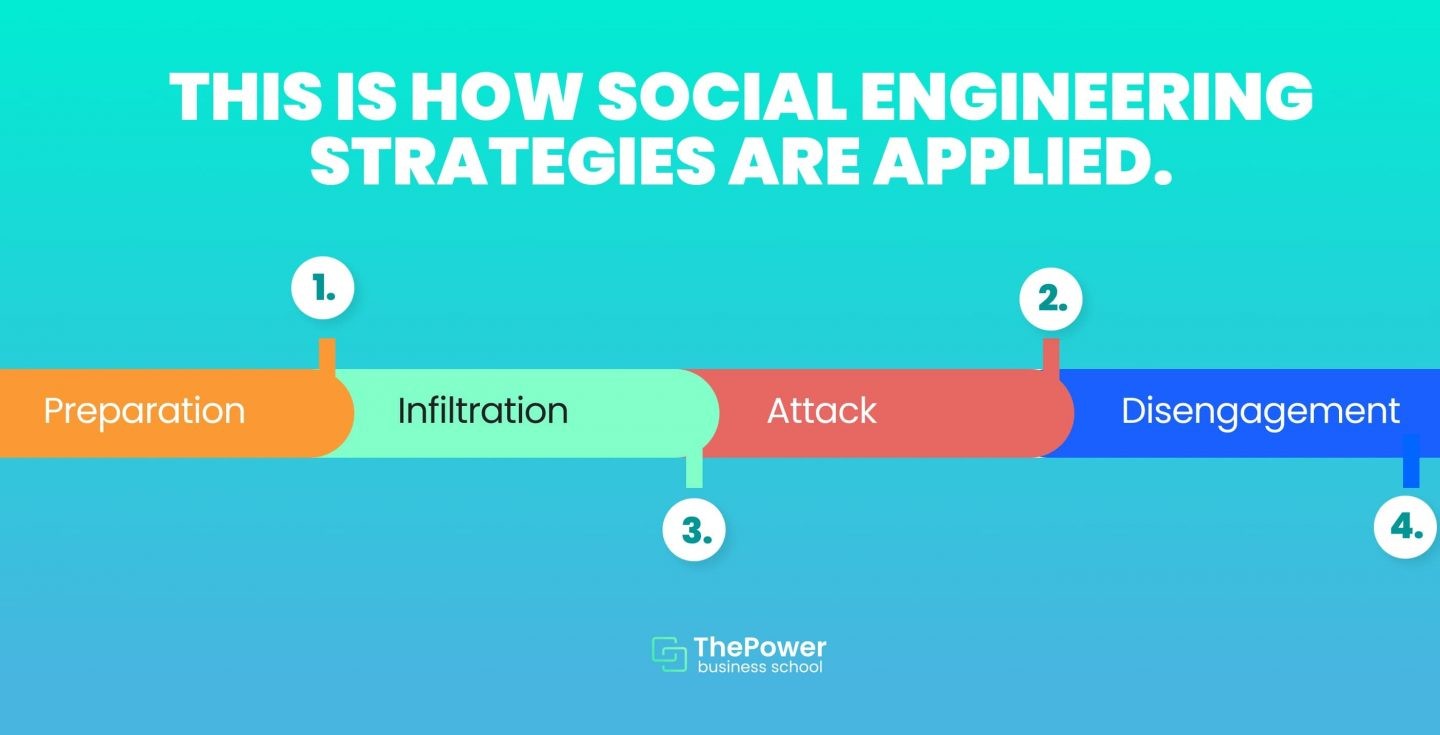
According to Kaspersky, social engineering strategies are usually executed as follows:
Preparation: the hacker gathers information about his potential targets, approach strategies, and the means he will need.
Infiltration: this is where the hacker seeks to establish a relationship of trust and credibility with his target.
Attack: the hacker casts his hook hoping to manipulate the victim into revealing the information he needs or the access he seeks.
Disengagement: once the user does what the attacker needs to hack the system.
With all this said, let's take a look at why social engineering is key among cybersecurity specialists.
Social engineering and its role in cybersecurity and ethical hacking.
Let's look at the data:
According to Verizon, 82 % of computer security breaches occur thanks to human error.
Furthermore, according to IBM, security breaches involving the human element amount to 95 %.
Since humans are the most vulnerable link in any system, cybersecurity specialists must also consider human error in all, absolutely all, of their strategies.
Cybersecurity specialists must stay 3 steps ahead of hackers, so they must hack their own systems to find any security gaps. And that includes users.
So if you want to specialize in cybersecurity, you need to know about small-scale and large-scale strategies, how to avoid them, and how to minimize potential security risks as much as possible.
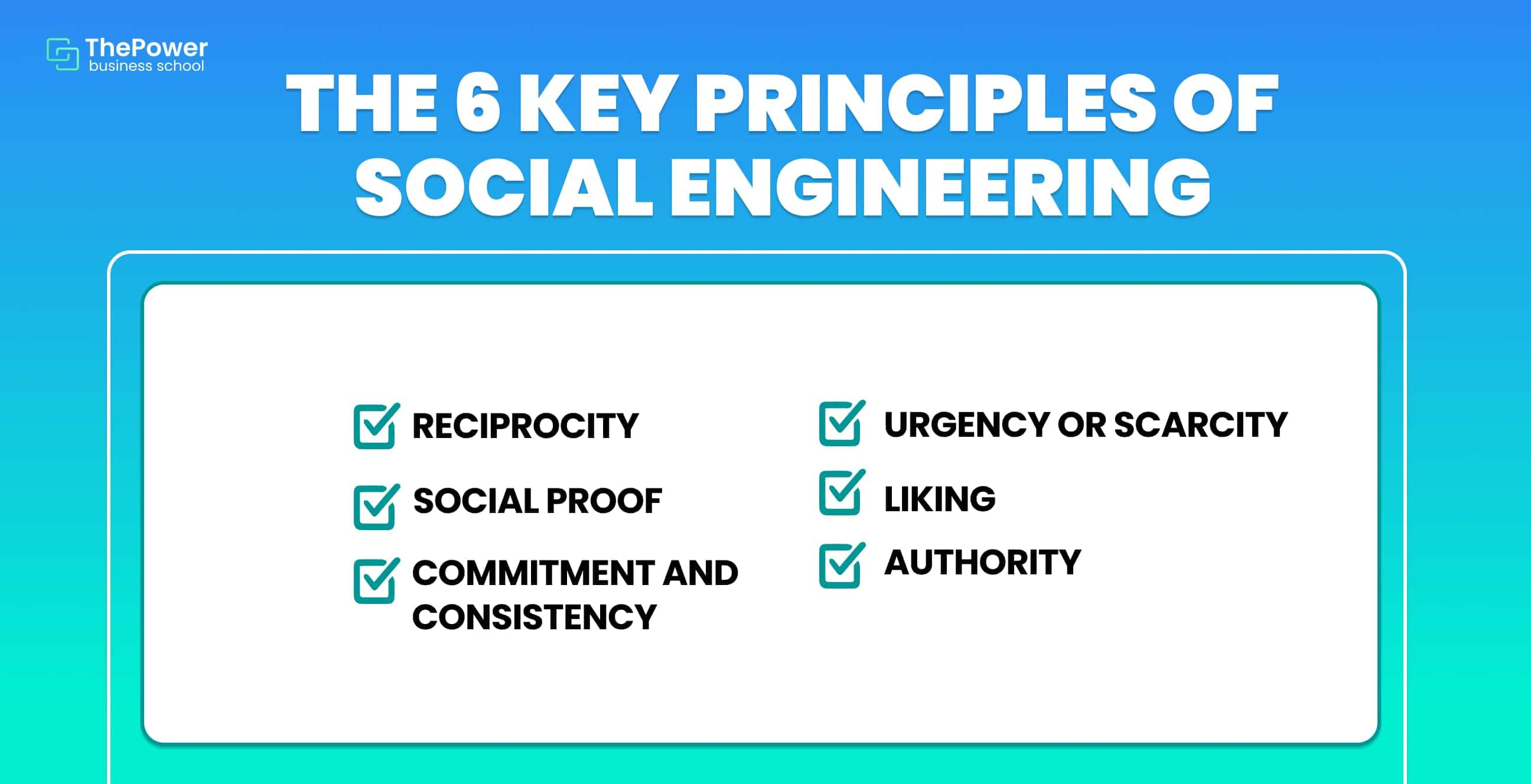
The 6 key principles of Social Engineering
Social engineering strategies are based on 6 fundamental pillars based on manipulating, deceiving, blackmailing, or coercing the user in order to hack him. These are:
1. Reciprocity
This is when hackers offer favors and rewards, from free samples to prizes of all kinds and colors.
This is one of the most exploited qualities in social engineering, hacking, and, of course, scams.
Reciprocity can also be used as a persuasion tool to convince the user to reveal confidential information. For example, a colleague who does you a favor and, in return, asks you for privileged access to return the favor.
2. Social proof
The proof is quite effective when it comes to implementing social engineering.
This principle is based on "people will do what other people do". Individuals tend to follow the crowd, masses tend to follow leaders. And likewise, a user does what other users do.
In this case, hackers and scammers can use fake stories, testimonials, numbers and statistical data to give credibility to their manipulation tactics. Thus, they trick other users into accessing pages where they can steal their data, among other strategies.
3. Compromise and consistency
This principle consists of tricking the victim into accepting a commitment and blackmailing or manipulating him or her with that commitment.
This commitment involves the user's admiration, loyalty or even love for superstars, sports teams, charities, laws, political parties, and even philosophical, religious, and spiritual ideals, among many others.
A social engineer can leverage the nexus of his potential victims to exploit that sense of commitment. For example:
He can create a fake charity campaign to exploit his recipients' sense of commitment. And thus, through engagement, convince them to hand over their personal and financial data.
4. Urgency or scarcity
This principle is quite simple but extremely effective.
Limited offers are much more tempting and irresistible thanks to the time factor. After all, no one wants to miss a great opportunity or pass up an excellent offer.
Many hackers take advantage of the sense of urgency and scarcity to present products, services, and prizes as unbeatable opportunities. And so, they seek to convince their targets to access pages, fill out forms, or provide sensitive information impulsively.
5. Liking
Empathy and familiarity can be quite powerful and efficient manipulation tools.
Let's look at it this way:
It’s easier to manipulate people through something or someone they like or find attractive or familiar.
Both physical attractiveness, familiar faces and objects, and products presented as irresistible prizes are powerful tools for scams and cyberattacks. Tools that, in many cases, can go unnoticed by the user.
This is the same principle used in advertising to captivate and catch the attention of the public and potential customers.
6. Authority
On the one hand, authority generates trust, respect, and credibility. On the other hand, disobedience to authority is synonymous with punishment, so many prefer to follow authority no matter what, even if they must go beyond their responsibilities and limits.
Many hackers pose as managers, bosses, associates, executives, and even friends of executives. And although it may seem hard to believe, many users take the bait and provide them with vital information that they would not otherwise give up.
Many users fall for this type of deception both out of respect for authority and fear of the consequences of disobeying.
6 social engineering techniques and how to avoid them
1. Baiting
This is the classic method used by fraudsters to seduce their potential victims with incredible offers that are very difficult to refuse. And of course, it’s one of the preferred techniques in social engineering.
Hackers and scammers can apply baiting through many platforms, such as emails, chat messages, social media links and misleading ads, among others.
Attackers can use a wide arsenal of techniques to carry out their baiting strategies, but the most common are: limited offers, prizes, sweepstakes and contests.
2. Quid pro quo
Something for something. This technique is based on manipulating the user through favors, retribution and reward.
For example:
A hacker may impersonate a customer service agent, offering technical assistance to tell his victim that there is a problem with his computer and he can help him solve it.
This is where the hacker explains that he will need the password and credentials to access the system. And since he's only looking to do you a favor, it raises less suspicion on the user.
3. Tailgating
Tailgating is a physical hacking technique, where the attacker tricks his victim to infiltrate private installations, protected by security systems.
In other words: real infiltration.
The tactic is simple but effective. It consists of following a target to gain access to a restricted area. The attacker can also directly trick his target into letting him in, and this is where social engineering comes into play.
For example:
A hacker can pose as a visitor or an acquaintance of one of the employees.
He can also pretend to be a contractor called in to make repairs.
Or again, he can pose as a delivery driver and gain access to a locked building directly, either through the reception, parking lot or loading dock.
4. Scareware
Consists of using fear to manipulate the victim into revealing confidential information without even thinking about it.
In other words:
Convincing the victim that their computer has a virus or a serious problem that needs to be resolved as soon as possible.
Hackers can also contact their targets and tell them that they are under computer attack or that there is an emergency within their system.
5. Phishing
This is one of the best-known and most effective strategies of social engineering, and also one of the simplest.
It consists of sending messages, emails and SMS, and even making calls to "fish" for recipients. In these cases, attackers pose as employees, agents or executives of legitimate institutions, such as banks, companies and governments.
In this way, attackers seek to present themselves as authority figures and trick users into giving them passwords, credentials, bank accounts and any type of confidential information that they can use to their advantage.
6. Pretexting
Pretexting is one of the most elaborate social engineering strategies. It consists of creating complex scenarios and scripts for those scenarios. Thus, scenarios where hackers can better manipulate their potential victims and gain their trust.
In these cases, attackers can present themselves directly to victims in order to get them to voluntarily disclose their confidential data.
Attackers can pose as high-profile professionals to target CEOs, executives and managers. Also to attack low-level employees, posing as executives, senior managers, associates and customers.
For example:
Hackers can pretend to be accountants, managers or human resources agents to ask for identity confirmation from potential victims.
They can also impersonate important customers to obtain privileged information.
Note: this strategy is quite similar to phishing, but is more focused on gaining the user's trust to obtain information. Phishing is more focused on manipulating the user to do a specific action.
How to detect possible Social Engineering attacks
There are 4 fairly easy-to-spot red flags that you can't overlook:
Too good to be true: if the offer seems too good to be true, it most likely is not.
The unknown sender or sender is unknown: research your new contacts on the web well. Make sure they are real people, check their social networks and check whether or not there are any suspicious elements.
Links and attachments: these elements are the most effective when it comes to cyber-attacks.
The message does not seem real: if it looks strange or simply does not seem real, it is best to assume that it’s not.
And of course, if any element makes you suspicious, it’s best to trust your instincts and act carefully. And to that end, we'll give you some tips as a gift below.
Additional tips and countermeasures to avoid social engineering
Before concluding, some simple and easy-to-apply but extremely effective tips to prevent manipulation and social engineering techniques.
For emails and social networks
Never click on links in emails or messages: just by clicking on them, you could let a virus into your computer. And it could steal your personal and financial data.
Use two-factor authentication: this is a simple method, but it can block the vast majority of cyber-attacks and attempts to access your online accounts.
For your devices and passwords
Remember to use different devices and accounts: if you keep all your passwords and recovery numbers on the same device, a hacker could access all your accounts through it.
Use VPNs or proxy servers: this way, hackers will not be able to track the IP addresses of your devices and you will become a much harder target to attack.
Don't share your Wi-FI password: this is a fairly easy access point to exploit, just like public Wi-Fi networks.
Never share passwords (or other sensitive data): no matter what the situation, never reveal your passwords. And if an unknown person or company asks you for your personal, financial or business data, do NOT share them without investigating them.
For your software
Install an antivirus and security system: the vast majority of phishing attacks can be blocked with an up-to-date antivirus. These will prevent you from opening suspicious links or pages and will warn you of possible viruses or intruders on your system.
Keep your system updated: not only your antivirus but also your firewall, applications, and operating system.
And the most important thing
Remember to be cautious, prudent and cautious, and avoid sharing confidential or potentially harmful information with strangers. And always do thorough research before giving out personal or financial data.
Follow these tips and you'll minimize the risk of social engineering attacks and strengthen the security of your devices and networks.
And if you're interested in pursuing a career in cybersecurity, take a look at our training programs. We have a variety of training and resources for technology specialists.
If you enjoyed our article, don't forget to comment and share it with your contacts. Let us know your doubts or suggestions in the comments section.
Jun 26, 2023








